How Do Solar Watches Work? | What is Eco Drive Technology?
Solar power is becoming more and more popular as renewable energy sources grow in demand. Many devices in our homes now feature solar panels to make use of sunlight, including some wristwatches. How do solar watches work though? It seems like magic after all!
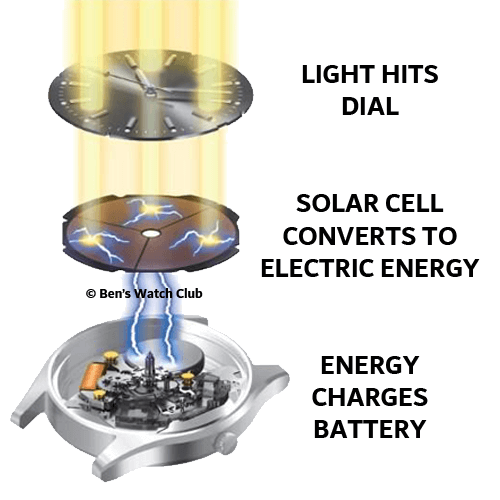
Solar watches work by converting light energy into electronic energy, via a specially designed photovoltaic system; akin to that used in a traditional solar panel. You’ll sometimes see this technology referred to as ‘eco-drive’.
When light energy hits the solar cell, typically positioned right beneath the surface of the watch dial, it induces an electric current by stimulating ‘free electrons’ present within the panel. This electrical energy is then passed to a battery, where it can then be stored and slowly released to power the watch.
You’ll often see solar watches referred to as ‘solar quartz’ watches. This is because the rest of the movement essentially operates in the same way as a traditional quartz watch; featuring a vibrating quartz crystal in the circuit, which ensures accurate timekeeping and a beat rate of one tick per second.
Unlike traditional quartz movements, which feature disposable batteries, solar-powered watches house rechargeable batteries; often in the form of lithium-ion cells. These can be recharged hundreds, potentially thousands of times before a replacement battery is necessary.
Due to the impressive efficiency of this technology, a single full charge can usually provide many months worth of power reserve; even if the watch is then stored in a dark environment.
Do solar watches last forever?
In addition to the long power-reserve, solar watches typically have an extended battery life compared to regular quartz watches, which often need changing in around 2-3 years. In many cases, you can expect upwards of 7 years of usage with a solar watch; though online there are many reports of such pieces lasting well over 20 years without a battery change.
Unfortunately, the batteries within solar watches will not last forever. The inherent nature of cells means that at some point they will almost certainly suffer from corrosion and degradation. Nevertheless, these can be changed at a marginally higher cost than batteries in most other wristwatches.
While solar watches can be stored in dark environments, for maximum long-term endurance it’s best to store them in reasonably well-lit areas. This prevents the battery from depleting to extremely low levels, which can harm its longevity.
Additionally, as with all watches, the functionality of solar watches will be inhibited by factors such as rust, water damage and dirt; whereby the battery, circuit or solar cell could become compromised.
Do solar watches work with artificial light?
While solar watches recharge best in natural lighting conditions, they can also be charged via some types of artificial lighting. While sunlight will comfortably yield the fastest charging speeds; some bright manmade light sources can provide enough intensity to slowly fill up the solar cell. It’s worth consulting the manual that comes with your watch, for more information on how your particular model responds to different lighting conditions, as this will vary from model to model. Generally, the brighter and closer the light source is to the watch, the better.
Photo Credit: Flikr
How do you know the charge level?
Most solar watches will inform you of their low charge level by including some sort of additional functionality. Solar-powered digital watches will often have a power level visual indicator as a part of the display; whilst analogue watches typically have specific functions associated with the second hand. For example, the ticks may operate in bursts of two when the charge level is low. Once more, this will vary from model to model, so the manual will come in very useful.
Photo Credit: Wikimedia
Are solar watches better than automatic or quartz?
While solar watches are almost always a better option than quartz watches due to the recharging capability it’s hard to compare them with automatic/mechanical watches, which offer a fundamentally different experience.
Solar watches are much more accurate than mechanical watches and have a significantly longer power reserve. Practically, they are the obvious choice. Nevertheless, automatic watches provide a smoother second hand, which is aesthetically more pleasing; along with arguably a higher level of craftsmanship due to the complicated mechanism within.
When were Solar watches invented?
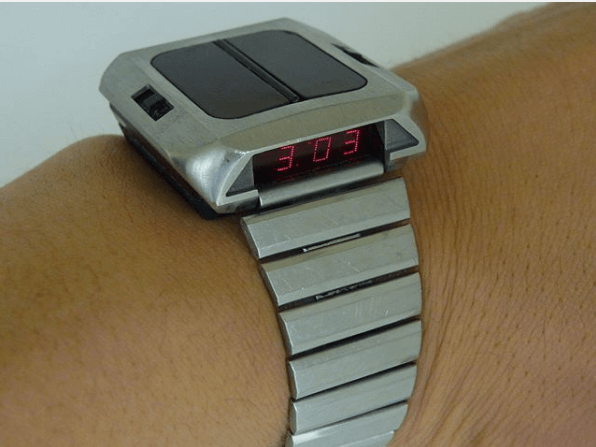
Following the release of the first quartz watch in 1969, the first commercially available solar watch came to market in 1972, in the form of the Riehl ‘Synchronar’. This unusual early LED digital watch featured two large solar panels across the surface, with the time being showcased in a small window on the side of the case (just above the bracelet).
Riehl ‘Synchronar’ Credit: Pinterest
The first analogue solar watch came in the form of the 1976 Citizen Crystron. As with the Synchronar, this model featured visually obvious solar panels across the design, rather than the near-invisible ones we see today.
Over the decades, technological advancements have resulted in much more efficient solar systems that allow watches to be charged faster and last longer. Citizen, in particular, now have a whole range of watches utilising this popular ‘eco-drive’ technology.
Solar Watches Pros and Cons
Pros:
Low environmental footprint
Cost-effective in the long run
Huge power reserve off a single charge
Very low maintenance
Can fit into a slim watch case
Very accurate
Cons:
Typically more expensive than regular quartz watches
Lower beat rate than mechanical watches